Comprehensive Overview of Eyelid Anatomy
Jump To
Our eyes are likely the most important vital structures we have in our body. The eyelids protect those eyes… serving multiple purposes including protecting the eyeball from injury, controlling the amount of light that enters the eye and also constantly lubricating the eyeball with tears secreted by the lacrimal gland during blinking. All these functions together help maintain the structural integrity of the eyeball and protect them from external influences.
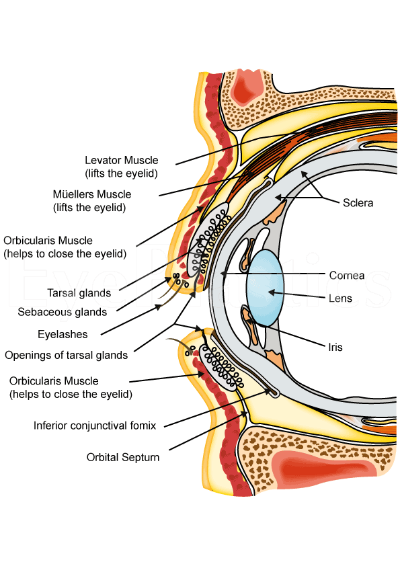
From an anatomical point of view, the eyelid consists primarily of skin, soft subcutaneous tissue and a thin layer of muscle called the orbicularis oculi. Under this muscle is the septum which includes the fibrous orbital septum and tarsi. The eyeball is covered by a thin layer of tissue called the conjunctiva, and fat tissue aids in protecting it. In more detail, a sagittal section taken across the eyelid can offer a clear view of the various structures that form it. The tissues can be divided into planes by structures called the septum. The orbital septum differentiates the orbital tissue from the lid. Behind the septum are a number of different other structures, a knowledge of which is essential if surgery is to be performed. In particular, it is essential to identify the anterior and posterior lamellae. The anterior lamella consists of the skin and the orbicularis oculi muscle while the posterior lamella consists of the conjunctiva and the tarsus.
The Structure of the Eyelids
The upper eyelid starts at the eye and extends upwards joining the skin of the forehead and is distinguished from the forehead skin by the presence of eyebrows. Similarly, the lower eyelid starts at the eye and extends to join the skin of the cheek. Upon inspection, it is evident that the lower eyelid is looser (laxity) than the upper eyelid, particularly because the tissue within the cheek that blends with the lower eyelid is more dense.
At the top of the upper eyelid is a fold in the skin called a superior palpebral sulcus (skin crease). It lies approximately 8 to 11 mm above the margin of the upper eyelid and consists of levator aponeurosis fibers. Similarly, the skin fold in the lower eyelid is called the inferior palpebral sulcus. This lower skin fold is often more prominent in children and can become less prominent as one gets older. Anatomically, the inferior skin crease is seen around 3 to 5 mm below the outer aspect of the lid margin.
The inner aspect of the eyelid is called the inner canthal region. At this region runs a fold of skin called the nasojugal fold. From an anatomical point of view, this fold lies between the orbicularis oculi and the levator labii superioris. The nasojugal fold is that area of the inner aspect of the eye where tears roll down and can accumulate (also called the tear trough). Similar to the nasojugal fold, the outer region of the eyeball is called the malar fold and runs from that outer location towards the nasojugal fold.

When the eyes are open, the space between the upper and lower eyelids is typically described as ‘fusiform’, or the palpebral fissure. Typically, the palpebral fissure measures between 28 to 30 mm wide and around 9 to 10 mm in height. When young, upper eyelids lie slightly higher than older individuals. There are two points at which the upper and lower eyelids meet. The one on the inner aspect is called the medial canthus and the one on the outer aspect is called the lateral canthus. Both of these have unique angles. When examined along a horizontal plane, the medial canthal angle is located around 2 mm lower than the lateral canthal angle in Caucasians (3 mm lower in Asians). The nose lies around 15 mm on the inside of the medial canthus. In summary, the palpebral fissure consists of the medial and lateral canthus, the lacrimal papillae (part of the tear glands, also called lacrimal glands) and a small opening of the lacrimal glands through the lower eyelid at the medial canthus called the punctum lacrimale.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue of the Eyelids
The eyelid is primarily made of skin. It is the thinnest skin in the body and is less than one mm thick. Within the skin are a number of glands called sebaceous glands that secrete an oily substance called sebum. These glands are in larger numbers at the nasal aspect of the eyelid. At the junction between the eyelids and forehead/cheek, the texture of the skin changes and becomes a lot thicker. Below the skin is a layer of thin connective tissue called a subcutaneous tissue (sub = under, cutaneous = skin). Underneath the skin, along with the subcutaneous tissue is a thin layer of fat. Typically, subcutaneous tissue is absent at points where the skin is attached directly to underlying ligaments such as the medial and lateral palpable ligaments. The skin and subcutaneous tissue can be subject to certain clinical conditions such as dermatochalasis and blepharochalasis.

Orbicularis Oculi Muscle Function
The orbicularis oculi muscle plays an important part in the function of the eyelids and also in facial expressions. When it contracts and relaxes, the skin over the muscle moves as well. The orbicularis oculi muscle is attached to the skin through tissue that forms the superficial musculoaponeurotic system.
Broadly divided, the orbicularis oculi muscle consists of two main parts. The orbital part plays a role when the eyelids need to be tightly shut. It is further divided into pretarsal and preseptal segments. The other part is called the palpebral portion that plays a role in winking and blinking. The muscle is supplied by the facial nerve then divides into different branches to supply these different muscles. Anatomically, the facial nerve travels under the muscle groups and supplies it from under the surface.
The orbital part of the orbicularis oculi muscle is linked with other muscles responsible for facial expression. It originates from the inner margin of the orbit, further attaching to the upper and inner aspect of the orbital bone. The muscle fibers interact with the surrounding facial muscles (corrugator supercilii and frontalis muscle). The preseptal portion of the orbicularis oculi muscle consists of a superficial and deep muscle. The fibers that lie within the upper/lower eyelids join to form a structure called the lateral palpebral raphe. The pretarsal portion also has similar origins and its fibers run under the lateral palpebral raphe, running into a bony structure at the outer aspect of the orbital bone called the lateral orbital tubercle through the lateral canthal tendon.
Submuscular areolar tissue
The submuscular areolar tissue is a loose connective tissue that lies beneath the orbicularis oculi muscle. It forms an anatomical plane that divide the eyelid into a front (anterior) and back (posterior) portion. The fibers of the levator aponeurosis pass through this plane in the upper eyelid. A small portion of these fibers contribute towards the development of the upper eyelid crease. Similarly, in the lower eyelid, the fibers of the orbitomalar ligament passed through this plane. If this anatomical plane were to be tracked towards the eyebrow area, the retro-orbicularis oculi fat will be traversed. If the plane were to be tracked towards the cheek, the sub-orbicularis oculi fat would be traversed.
Tarsi and Orbital Septum Structure
Tarsal plates
The tarsal plate exists to help the eyelids maintain their shape and integrity. The tarsal plate is dense and fibrous tissue around 1mm thick and 29 mm in length. There are two main types of tarsi – the superior tarsus and inferior tarsus. The superior tarsus is crescentic in shape and measures around 10mm vertically in its central aspect. It narrows outs as it traverses towards the nose and outer aspect of the eyelid. Its lower area is what forms the back of the eyelid that lies next to the conjunctiva of the eyeball. Similarly, the inferior tarsus lies in the lower eyelid, measures 3.5 to 5mm in height at its center, and also lies in contact with the conjunctiva. Each of the tarsi are attached to the margin of the orbits through the medial and lateral palpebral ligament. Within the tarsal plates are 25 tiny glands called mebomian glands. These glands are as tall as the tarsus, and they open at a point just in front of the lid margin where the conjunctiva meets the skin (mucocutaneous junction). If one were to look closely, they lie behind a grey line on the margin of the eyelid.
Medial and Lateral Palpebral Ligaments
Also called the medial canthal tendon (MCT), the medial palpebral ligament is a band of fibrous tissue that holds the inner aspect of the tarsal plates in place. It is closely related to the orbicularis oculi muscle and the tear ducts. The MCT is composed of an anterior limb which is formed by a small part of the superficial aspect of the orbicularis muscle that lies behind the tarsus. It traverses along a horizontal plane but is also attached to the frontal bone through a superior extension. The deeper part of the orbicularis muscle lies behind the lacrimal crest and the lacrimal sac fascia. The fascia of the lacrimal sac is therefore closely related to the MCT.
Lateral palpebral ligament
Also called the lateral canthal tendon (LCT), the lateral palpebral ligament is also a band of fibrous tissue that originates from the tarsus, traversing outwards under the orbital septum and eventually into the lateral orbital tubercle. The LCT is around 10.5mm long and 6.5 mm wide. The orbital septum and the LCT are separated by a pocket of fat called the Eisler pocket. The LCT is attached to the outer part of the orbital rim through a superficial plane of fascia. This is also called the superficial lateral canthal tendon and helps to keep the lateral canthus stable.
Orbital septum
A septum often refers to a band of tissue that separates a structure. The orbital septum is a connective tissue band that attaches to the border of the orbital bone at the periosteum (outer aspect of a bone). Within its central structure, the septum joins the lid retractors at the lid margins. Looking at the septum in more detail, we find it contains a number of layers (lamina) that are in close relationship with the anterior connective tissue framework. From a functional point of view, the septum has mobility similar to the eyelids. If one were to trace the septum in an outward direction (laterally), it is evident that it is attached to the margin of the orbit, around 1.5 mm in front of the attachment of the LCT. The orbital septum is separated from the LCT by the previously discussed Eisler’s pocket of fat. While traversing laterally, the septum runs along the rim of the orbit at the arcus marginalis. When traversing above and towards the nose, the septum runs across the supraorbital groove, in front of the trochlea and along the posterior aspect of the lacrimal crest. From an anatomical point of view, this position results in the septum lying in front of the medial ligament and behind the lacrimal sac and Horner muscle.
When tracing the attachment of the septum, it passes the lacrimal sac fascia, eventually reaching the anterior lacrimal crest at a point corresponding to the lacrimal tubercle. It then passes below this crest and along the lower rim of the orbit ultimately leaving the rim at a point beyond the zygomaticomaxillary suture. This results in creation of a small space (recess) due to its separation from the zygomatic bone – called the premarginal recess of Eisler, and is filled with fat. Eventually, the septum reaches the lateral orbital margin at a point that lies just below the Whitnall ligament. Another extension of the septum exists from the point where the orbital septum joins the levator aponeurosis. Described by Reid et al, this extension travels over the tarsal plate and ultimately reaches the ciliary margin. The function of this septum is to aid the levator aponeurosis, and is considered while operating on the eye.
Orbicularis retaining ligament
Also called the orbital retaining septum or orbitomalar ligament, this ligament attaches the orbicularis oculi muscle to the lower rim of the orbit. It is weak in its central aspect and stronger in the lower-outer aspect. When traced laterally, it is contiguous with tissue that is formed by fusion of the outer part of the orbicularis oculi and the deeper periosteum and temporalis fascia. This fusion is called the orbital thickening. This orbital thickening covers the frontal process of the zygomatic bone. As one gets older, the orbicularis retaining ligament tends to get thinned out and stretched, with these changes more prominent in the central aspect. When excised along with the orbital thickening, there is a full release of the superficial fascia that lines the orbital rim.
Upper lid retractors
The upper lid retractors are a group of muscles whose main function is the keep the upper eyelid elevated. The muscle that forms a part of this is called the levator palpebrae superioris (LPS). This muscle originates from the bottom aspect of the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone located within the skull. It consists the levator muscle and the superior rectus muscle, and are joined together by fibrous tissue. From its origin, the LPS traverses horizontally forward for about 40mm, ending in an aponeurosis that is around 10mm posterior to the orbital septum. It then takes a more vertical course toward the Whitnall ligament (superior transverse ligament).
The Whitnall ligament is similar to the previously described orbital fascia and lies in close proximity to the aponeurotic and muscular junction of the LPS. It extends around the upper margin of the orbit in a plane that lies between the lacrimal gland fascia and the trochlea. The LPS varies in thickness, and is relatively thin in areas between the upper orbital rim and the Whitnall ligament. When traced inwards and outwards, the LPS aponeurosis forms ‘horns’ called medial and lateral horns. The lateral horn runs through the lacrimal gland, dividing into two lobes – the palpebral lobe and the orbital lobe. It goes on to attach to the lateral retinaculum located at the lateral orbital tubercle. The aponeurosis eventually reaches the border of the superior tarsal plate having fused initially with the orbital septum. At the bottom end of this fusion, a small part of the aponeurosis attaches to the lower aspect of the anterior part of the tarsal plate. One part of this fusion extends forwards to insert into the pretarsal orbicularis oculi muscle and skin, resulting in the formation of the skin crease in the upper eyelid.
Eyelid Fat Pads
There are a number of different fat pads that are present within and around the eyelid. One layer of fat called the pre-aponeurotic fat is found right behind the orbital septum and in front of the levator aponeurosis. Also within the upper eyelid are two more fat pads that are centrally and medially (towards the nose) located. The medial fat pad is pale yellow in color and lies in front of the levator aponeurosis, while the central pad of fat is broader and a deeper yellow color. As it travels outwards, it wraps around the inner aspect of the lacrimal gland. The lacrimal gland can be clearly seen and differentiated from this fat by its pink color and lobulated structure. The lacrimal gland is positioned posteriorly to the orbital margin but might prolapse slightly making it more prominent when the eye is examined.
While the above described the fat pads are within the upper eyelid, the lower eyelid fat pads are slightly different in structure. The inferior oblique muscle separates the central fat pad from the medial fat pad. There is a small amount of fat that lies in front of the inferior oblique muscle as well. The inferior oblique muscle originates from a small indentation in the lower border of the orbital floor, moving behind the orbital margin and at the upper aspect of the nasal lacrimal canal. It passes underneath the inferior rectus muscle and through the Tenon capsule, ultimately close to the macula of the eye.
Blood Supply to the Eyelids
The eyelids are supplied by branches of the internal and external carotid arteries. The ophthalmic artery branches off the internal carotid artery and supplies different parts of the eyelid. At the inner part of the upper eyelid, the artery splits into two and traverses outwards to supply both the upper and the lower eyelid. The branch that supplies the lower eyelid arises from the superior marginal vessel (that supplies the upper eyelid). The superior and inferior marginal vessels form the marginal arcade. The marginal arcade arteries are located at the front of the tarsus, 4 mm from the upper eyelid and 2 mm from the lower eyelid margin each. The superior marginal arcade gives rise to a peripheral arcade that runs in front of the Muller muscle, giving it a superficial plane and making it vulnerable during eyelid surgery. Another branch of the internal carotid artery is the lacrimal artery that passes through the orbital septum along each eyelid and ultimately joins the marginal arcade. While the above described the branches of the internal carotid artery, the external carotid artery supplies the eyelids as branches of the facial artery, infraorbital artery and the superficial temporal artery.
Lymphatic drainage
The lymphatic drainage of the eyelid is rather extensive. The majority of the upper eyelid and the outer half of the lower eyelid drain into the pre-auricular lymph nodes, while a small part of the middle of the upper eyelid and the inner half of the lower eyelid drains into the submandibular lymph nodes.
Muscles
There are numerous muscles around the eyeball that control of different movements. These muscles are called extraocular muscles. They include the medial rectus, lateral rectus, inferior and superior oblique and inferior and superior rectus muscles. These are responsible for the various directions of movement of the eyeball, including rotation of the eyeball. Within the eyelid, the levator palpebrae superioris is responsible for elevation of the upper eyelid.
The extraocular muscles are supplied by a variety of different cranial nerves. These include the oculomotor nerve, the trochlear nerve and abducens nerve.
Bones
The socket within which the eyeball is located is called the orbit. It is a pyramidal shaped fossa that is created by the fusion of different orbital bones. These bones originate from the different aspects of the skull such as the frontal bone, sphenoid bone, zygomatic bone and the Palatine bones. In adds to, the maxillary bone and the lacrimal bone also form a part of it. The arrangement of these bones is such that the walls are parallel to each other. The orbit measures 4 cm in height, 3.5 cm in width and is around 5 cm in depth.
Within the orbit are a number of blood vessels and nerves. These passed through the bone through various openings called fissures. There are three main openings – the superior orbital fissure, the inferior orbital fissure and the optic canal. Through these openings, various cranial nerves passed through and supply the muscles and blood vessels in the orbit. The superior orbital fissure allows for the passage of the frontal nerve, lacrimal nerve, nasociliary nerve and the recurrent branch of the lacrimal artery along with the superior orbital and ophthalmic veins. The inferior orbital fissure allows for the passage of the infraorbital nerve, zygomatic nerve, infraorbital artery and vein and parasympathetic nerve supplying the lacrimal gland. Through the optic canal passes the optic nerve, central retinal vein and ophthalmic artery.
Lacrimal gland
The lacrimal gland is responsible for tear production. It is divided by the levator aponeurosis into an orbital lobe and a palpebral lobe. It has a characteristic appearance as has been previously described. It is supplied by the lacrimal nerve which is a branch of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve. The lacrimal gland secretes tears that are drained through a series of ducts. The lacrimal system consists of lacrimal papillae, canaliculi, lacrimal sac and naso-lacrimal duct. The canaliculus joins the lacrimal sac at an angle which is protected by the valve of Rosenmuller.
Connective tissue
We have already taken a brief look at the different types of connective tissue that are seen in the eyelid and the structures around it. The fascia that is present around the eyeball divides the orbit into a number of different connective tissue planes. Within each of these planes lie different structures. Having a knowledge of the structures helps the surgeon in locating them.



