Treatment of Ptosis
Jump To
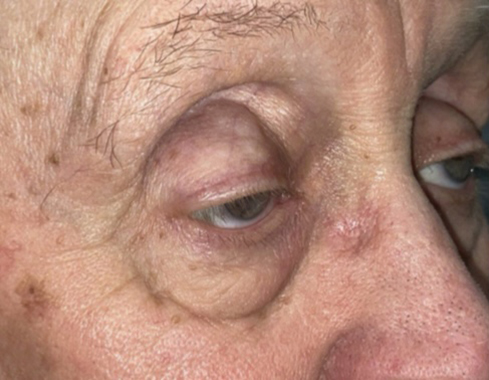
There are a variety of surgical procedures at Idaho Eyelid and Facial Plastic Surgery to correct congenital or acquired ptosis. Ptosis can result from apneurosis of the levator muscle, nerve abnormalities, trauma, inflammation, or lesions of the lid or orbit. Incorrect function of the levators can be caused by dysfunctional nerve communication. Ptosis can also result from myogenic, neurogenic, aponeurotic, mechanical or traumatic causes. It can be isolated, or part of other conditions, like immunological, degenerative, or hereditary disorders, tumors, or infections.
Ptosis is categorized by its cause. While acquired ptosis is most commonly caused by aponeurotic ptosis, congenital neurogenic ptosis is believed to be caused by Horner’s Syndrome. Ptosis can also be caused by trauma and other afflictions. These are briefly discussed below:
- Acquired ptosis can occur as a result of senescence, dehiscence, or disinsertion of the levator aponeurosis. Chronic inflammation, or intraocular surgery can also cause acquired ptosis. Wearing contact lenses for long periods of time can also lead this condition.
- Congenital neurogenic ptosis may be associated with ipsilateral ptosis, iris and areola hypopigmentation and anhidrosis due to the paresis of the Müller muscle.
- Traumatic eyelid lacerations can also cause ptosis. Transection of the upper eyelid elevators or disruption of the neural input can result in poor eyelid function.
- Other causes of ptosis include eyelid neoplasms, neurofibromas or the cicatrization after inflammation/surgery, or increased tendon laxity that comes with aging.
Levator resection (Anterior/External approach)
This treatment method is surgical and involves our surgeons making skin incisions to adjust the eyelid position. Patients can be awake during this process, and this surgery may be combined with upper and/or lower lid blepharoplasty.
Müller muscle resection (Poster / Internal approach)
The Müller muscle resection method leaves no visible skin incisions and can also be combined with upper and/or lower lid blepharoplasty. It is ideal for patients with minimal excess skin. Candidates for this procedure respond to 2.5% phenylephrine place behind the upper eyelid.
Frontalis sling operation
In more severe cases, the frontalis sling procedure is used to transfer the elevating function of the ptotic eyelid to the frontalis muscle. During this surgical procedure, the eyelid is directly suspended to the brow using various materials, thereby forming a sling from the frontalis muscle (brow) to the eyelid. The materials used are synthetic, such as ptoseup, Supramid suture, Gortex, silicone, or Mersilene mesh.